Conversion rate optimization is a systematic process of increasing sales on a website. CRO is both an art and science of converting visitors into buyers. CRO is used for improving a website so that it engages and converts more visitors to your key goals. — be that buying a product, filling out a form, or any other.
For instance, conversion on an e-commerce website will be ordering a product. For a gymnasium website, it could be signing up for a body transformation challenge.
The Conversion Rate Optimization process involves knowing how visitors move through the website. Therefore, a conversion always depends on the type of website and product or service. Statistics also say that very few sites are doing CRO, or they are doing it poorly.
Let us look at the crucial steps for the CRO program.
Step 1 – Data Gathering and Research
CRO requires us to gather data to inform the tests we are undertaking. Even though at this level, it can be quite a lengthy process. It is worth the time and energy investment.
We may begin with data by consulting the Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). For example, Customer Acquisition Cost, Sales Cycle duration, and Monthly Recurring Revenue.
We can then start considering other data points. Quantitative data like Organic Traffic, Average Session Duration, CTR rates, Bounce Rate, etc. Will give a clearer picture of the website usage.
Data analytics will give us metrics such as traffic sources, top pages. We can have a clear idea about sources that are performing well. A website may have a great website, but if it has poor traffic that does not convert. It won’t have many sales.
Data gathering is a continuous process as long as our website is active for business.
Step 2 – Hypotheses
We can describe it as a tentative assumption for trying out the empirical and logical outcomes of a given action.
In Conversion Rate Optimization, it could mean a working theory (depending on the data and research analysis) of “If I vary Y, then X will change.”
Once we have all the data, it will uncover some glaring issues on the site. After the website’s analysis, we could come across two types of problems.
- Problems that are immediately actionable.
- Problems that require testing and hence hypothesis.
Type “1” problems are usually technical. We can fix them without having to put forward any hypothesis on the. Such issues need to be fixed immediately.
Type “2” problems are more diverse. They may not have a single way solution. Hence hypothesis is needed.
For example, – Changing website Headlines to make them more specific and smart to get better results. There is no particular font, color, size, etc. to create the best headline. However, it has a significant impact on CRO.
Therefore, we need to monitor each iteration and keep improving it with the hypothesis for better results. In addition, E-commerce stores can set up session recordings for most significant pages on the website and see how they perform.
After building the list of hypotheses, e must prioritize it with the most urgent to the less pressing.
We will delve into the in-depth in the coming stages.
Step 3 – Prioritizing Ideas
Priorities guide our life choices and help us to make better decisions. The things we focus on describe who we are. The process of CRO this applies as well.
Prioritizing hypotheses and ideas does not help in solving the issues. Give attention to the most pressing need for the business. It creates precedence for future optimization tasks. If done with great care, we will have an efficient test system ready for everything to run.
Isn’t it a wonderful thing to Prioritize? Let us look at some of the well-known prioritizing structures! Not the sumptuous dessert but less for Potential for Importance, Ease, and Improvement.
Step 4: Testing and Implementation
Since we have prioritized the hypotheses and we understand what kind of most pressing tests. It is time to act on those hypotheses.
Ideally, game-changing CRO activities need an ideal tool at hand. For higher conversions on a website. Here are the few things that are a must for testing and improving conversion rates.
User Analytics
When it comes to CRO, a lot of data needs tracking. It gives us specific breakdowns of our data point. For example, visitors overview data, organic traffic sources, best-converting email campaigns, and device summary report.
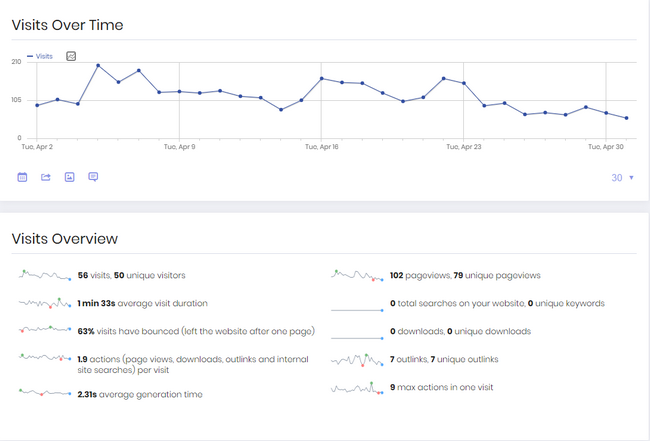
Page Performance
When a visitor first clicks on a website, he will notice how fast it loads. A business online will want visitors to have meaningful interactions with the website.
Performance is all about retaining visitors on the website. Websites check and study the performance metrics that work best to enhance the conversion rate.
Heatmaps
It is a platform that offers a click map to understand real-time user behavior. It helps us know the quality of leads and visitors that traffic brings. One can understand how CTAs or any significant links are working on the website.
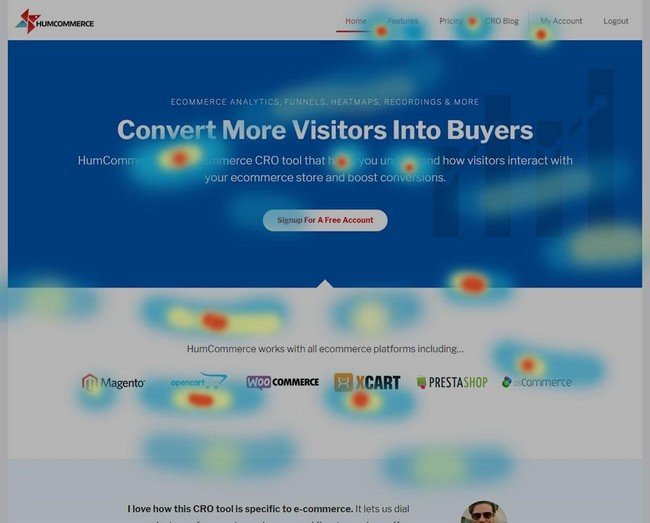
Create an optimization roadmap, run continuous experiments, and conduct visitor research. Heatmaps can identify frustration detection by identifying rapid clicks, dead clicks on the page. It then allows us to change what needs to improve on the site.
Session Recordings
It will allow us to see how exactly visitors navigate through the website. It gives us a stronger customer insight and analysis of on-page user behavior.
A/B Testing
It is among the number one experimenting platforms. It allows product and marketing teams to deploy tests and review digital experiences. Above all, A/B testing enables us to target the launch and to message in a more visitor-focused way.

It is difficult to find all the above functionalities in one place. But, if you have the Humcommerce CRO tool. You don’t need to find anything else for your e-commerce store.
It is one of the most comprehensive CRO – conversion rate optimization tools that provides behavioral analytics (Heatmaps, visitor session recordings, etc.) Besides conventional analytics (traffic source, traffic data, etc.).
This CRO tool enables you to change user experience through insight reports to increase conversions and engagement.
Step 5: Creating a Conversion Roadmap
When we make a list of common conversion problems (COP). We will need a roadmap to follow. We must address the central conversion problems first by looking at the data analytics, qualitative research, and also the heuristic analysis:
- Consider the areas of the website that are leaking the guests.
- Consider the health of various sections of the site.
- Learn the way visitors move from one section of the site to another.
Step 6 – Determine Issue Areas on the Webpage
Depending on the data collected, we have decided which page to optimize first.
We have done the polls, and we know some of the questions or concerns that visitors may have.
Do we have the information that visitors are looking for? Is the information displayed and well organized on that page with clarity?
Have you answered the questions visitors might have on certain things on that page? The good thing is you have done most of your work to assist you with identified issues on that particular page.
Step 7 – Analyze Pages With the Conversion Structure
How do you know the issues that are on the page?
This is for a 360 analysis to understand some of the problems identified on the page. This framework analyses all element of the page in the following areas:
- Confidence and Trust: Check if there are trust elements that are missing from that page?
- Incentives: Include incentives so that visitors can act in anticipation of a reward.
- Engagement: Could you include engagement elements to that page?
- Personas: If the page addresses different kinds of guest persona?
- Sales Sophistication: If the page provides all the information that page visitor requires to convert?
- Purchasing stage: Is the page that is designed for both early-in-the-funnel visitors as well as ready-to-convert guests?
The main reason for the framework is to determine whether:
- The element is not there.
- Elements are not identified and visible.
- If the element is present even though it is not effective based on the data.
- It is there and doing the required job.
Conclusion
Here, we learned the seven essential Steps of the CRO – Conversion Rate Optimization framework. For instance, a website needs relevant traffic for a good conversion rate.
Furthermore, we discovered many different ways to collect data. How to create a data-driven hypothesis, and we learned the need to put forward hypotheses. We also saw how to get those thoughts and put the ideas to the test using the ideal tools.




Comments are closed.